In modern society, the need for energy is increasing, so there is a never-ending search for electricity, which is cheap and sustainable. Following these concepts, we present the new source that manages to extract energy from the clouds. Let’s see what it consists of.
Electricity created from nothing: is it possible?
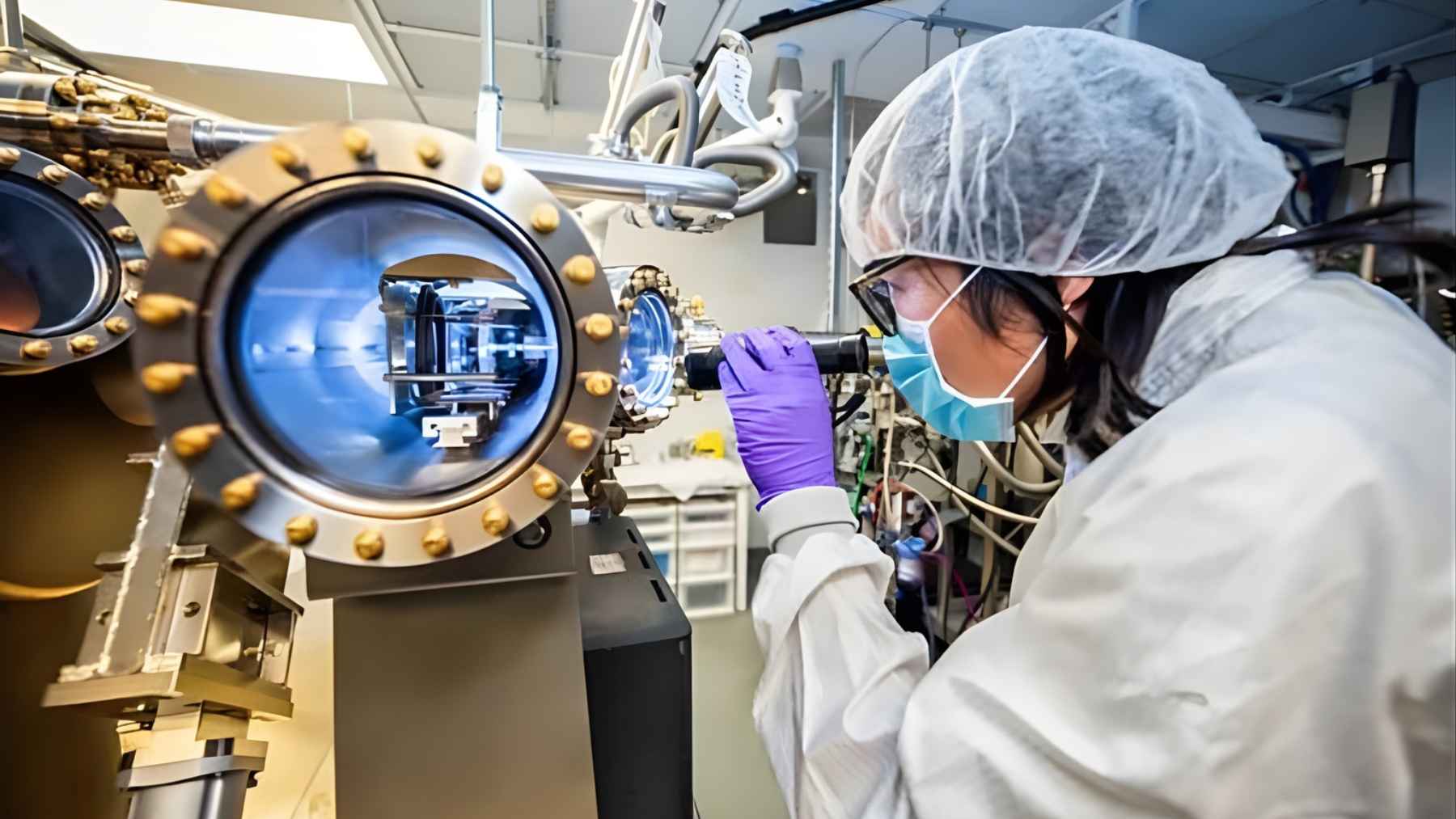
Staff at the University of Massachusetts developed, in early 2020, a device that uses protein from nature to generate electricity from “nothing”. Although this effective element is based on something very common: the moisture contained in the air.
The component was developed by a microbiologist and an engineer from the university’s research team. Basically, it was constructed with protein nanowires from a bacterium called Geobacter sulfurreducens. The element was christened Air-gen.
How the Air-gen works: It’s not science-fiction, but an unprecedented method to generate energy
Its mode of operation is very simple. When electrodes that are only a few microns thick are connected to the moisture, a small electrical force is generated. The best thing is that electricity can be extracted from almost any element or material.
So, the only one that would produce this effect (let’s call it Air-gen effect) is not the device, but any material that has a certain property can extract energy from air and humidity. The first application the creators came up with is to use clouds.
To do this, one must think of a cloud as consisting of countless water droplets. Each one has a certain charge and, when the environmental conditions are favorable, this electricity is discharged in the form of lightning.
The issue is that there is no way to capture this energy effectively. Therefore, what the device does is to generate a cloud, on a small scale, that produces electrical energy continuously, reliably and predictably so that it can be “harvested” for later use.
The core of this cloud is formed by a protein layer composed of nanowires of the aforementioned bacteria. This layer is dotted with nanopores that have an average diameter of 100 nanometers, which is less than one thousandth of a hair.
These nanopores form a free path that a water molecule must travel before it collides with another. But if this layer lets the aforementioned molecules pass from the top to the bottom, the first one will be bombarded by other molecules.
This action will create an imbalance, as in a cloud, which would generate very weak electricity. But if you add all these charges together, you get one of great magnitude. In this way, energy would be generated from the clouds or from nothing.
This technology is sustainable, renewable, non-polluting and very low cost. In addition, it has the capacity to produce electricity in very dry areas such as the Sahara desert, in others with very high humidity such as on the coasts and in the interiors of buildings.
Its incredible possibilities and applications in various sectors
The university researchers point out that clouds and air humidity are always found in all areas of the Earth and are very abundant. So energy can be available 24 hours a day, every day of the year, uninterrupted.
Therefore, it does not have the problem of intermittency that other renewable energies have. As for its applications, these are innumerable, being able to act as alternative and ecological energy, in medical equipment, smartphones, health monitoring sensors and many others.
In conclusion, you have seen how this revolutionary invention can extract energy from almost any element, such as clouds. Accordingly, it is a new source of energy that America can take advantage of.