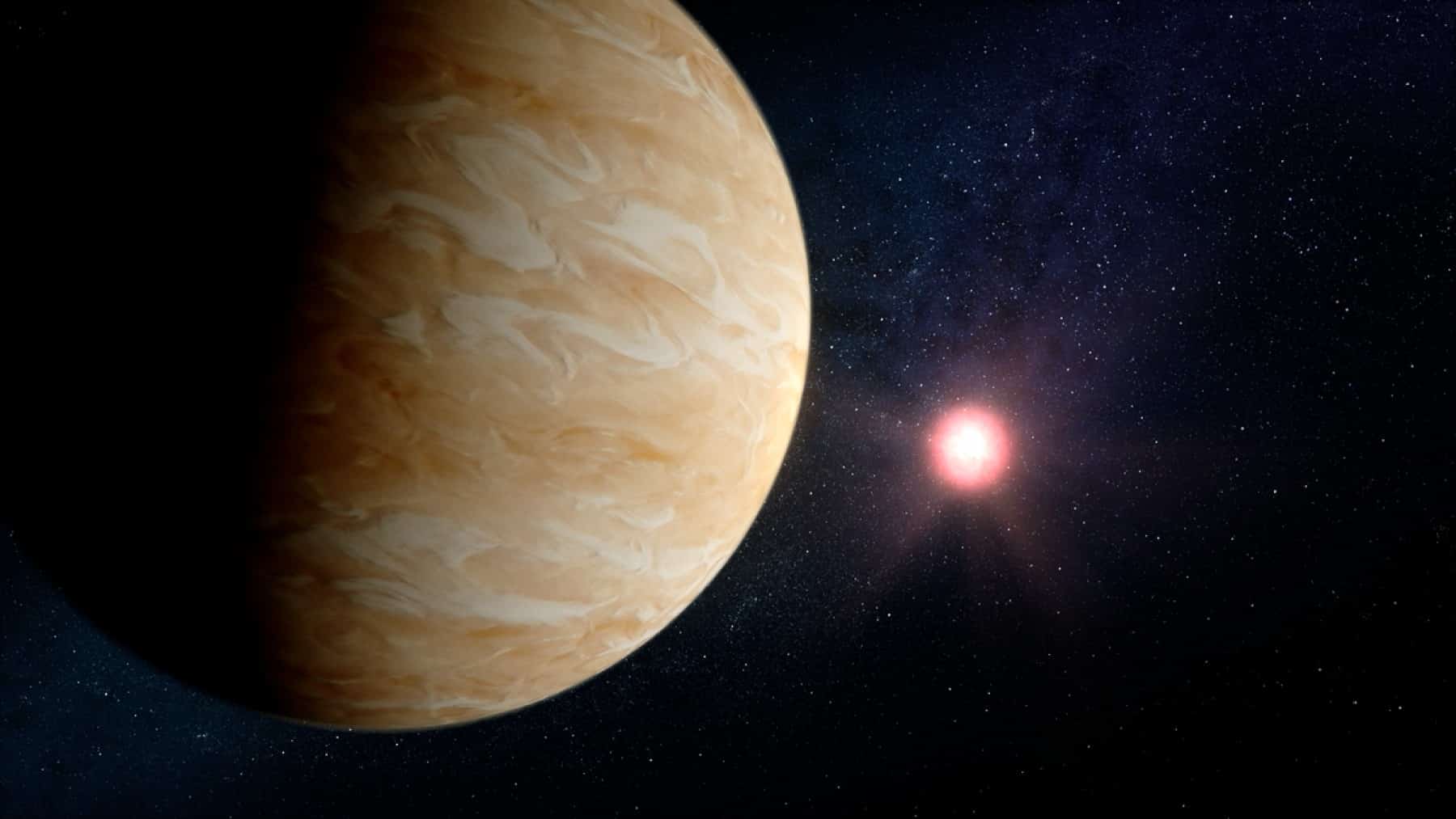
During their space observations, science experts identified the unconventional new planet, Enaiposha. This distant orbathing red dwarf star, at about 47 light-years distance from Earth, presents unique planetary attributes different from all known solar system planets. Scientific classification names the unusual planet “Super-Venus,” which changes our understanding of astrophysical characteristics while teaching us about planetary formation processes and atmospheric compositions.
Scientists found Enaiposha to have unusual characteristics that define its uniqueness.
The celestial body named GJ 1214 b or Enaiposha received a classification of mini-Neptune due to its planetary size and mass measurements. The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) observed Enaiposha and found that the planet shares attributes with the hotter and larger version of Venus. The discovery constitutes the first instance of identifying a “Super-Venus,” representing its own separate exoplanet type.
Scientists find it challenging to study this planet because its atmosphere produces thick and dense clouds. Scientists have verified the presence of major carbon dioxide levels in the planetary atmosphere, much like those found in Venus’s atmosphere. The data indicates that Enaiposha’s lower section of the atmosphere contains metal-rich components, yet the upper regions are laden with thick carbon dioxide and aerosol hazes.
Scientists have discovered the unconventional skies of an extra-planetary body.
The atmosphere of Enaiposha defies all atmospheric patterns that exist on known planets. Scientists identified that the atmosphere consists of hydrogen, helium, water vapor, methane, and carbon dioxide. A sophisticated atmospheric composition of Enaiposha was discovered by studying the starlight spectrum during the planet’s transit phase of Orkaria. The abundance of carbon dioxide is a distinctive feature that distinguishes Enaiposha from other sub-Neptune planets, making it an important research finding.
Due to its dense atmosphere and extreme heat conditions, Enaiposha remains a hostile place for life. Atmospheric research of Enaiposha enables scientists to understand atmospheric behaviors on habitable exoplanets and similar planets. Scientists have detected water vapor and complex metals in the atmosphere, which has prompted numerous questions regarding the planet’s developmental history.
This planetary research presents more difficulties than anticipated due to scientific obstacles that scientists encounter when studying it
Scientists face significant challenges while studying Enaiposha because the dense atmospheric haze blocks observers from seeing through most areas of the planetary atmosphere. The shroud of haze prevents scientists from collecting distinct spectroscopic data; thus, they need multiple observations supported by sophisticated modeling approaches. JWST detected faint signature signals that delivered essential details about the planet’s atmospheric makeup.
Staff members Everett Schlawin from the University of Arizona and Kazumasa Ohno from the National Astronomical Observatory of Japan dedicated extensive theoretical modeling work to understand the received data. The research indicates that Enaiposha contains a higher metal content and lower hydrogen levels than predicted. Identifying this planet challenges knowledge about sub-Neptune planets as scientists require additional advanced observational techniques.
New developments about Enaiposha will direct future research paths within exoplanet science
Research on exoplanetary studies gains major consequences from learning about Enaiposha’s classification as a Super-Venus. Planet science research suggests that numerous space bodies exist with complex atmospheric mixtures that cannot be assigned to standard planetary types. Astronomers should expand their exploration of planetary diversity because this new discovery motivates them to evaluate alternative theories about planetary development.
The special composition of Enaiposha serves both existing theoretical models and observational measurement techniques so they can be improved. Scientific research on this planet enables scientists to enhance their knowledge regarding atmospheric systems and produce enhanced techniques for discovering and analyzing exoplanets. Research activities will support space investigation toward identifying habitable planets and detecting extraterrestrial life forms.
Research into exoplanets has greatly advanced by identifying Enaiposha as a Super-Venus. Observing Enaiposha provides unique insights into planetary science and shows the diverse range of planets in the universe. Modern astronomers studying both Enaiposha and other exoplanets will inevitably discover new discoveries that will advance our comprehension of cosmic phenomena.