It’s a fact that when we discuss the high temperatures that the planet has been facing in recent years, it does not even cross our minds that something could reach 142 nonillion ºC. After all, this is the limit of possible heat that scientists have established. We are talking about the Planck temperature (~10³² K).
Have you ever wondered how hot the universe was right after the Big Bang?
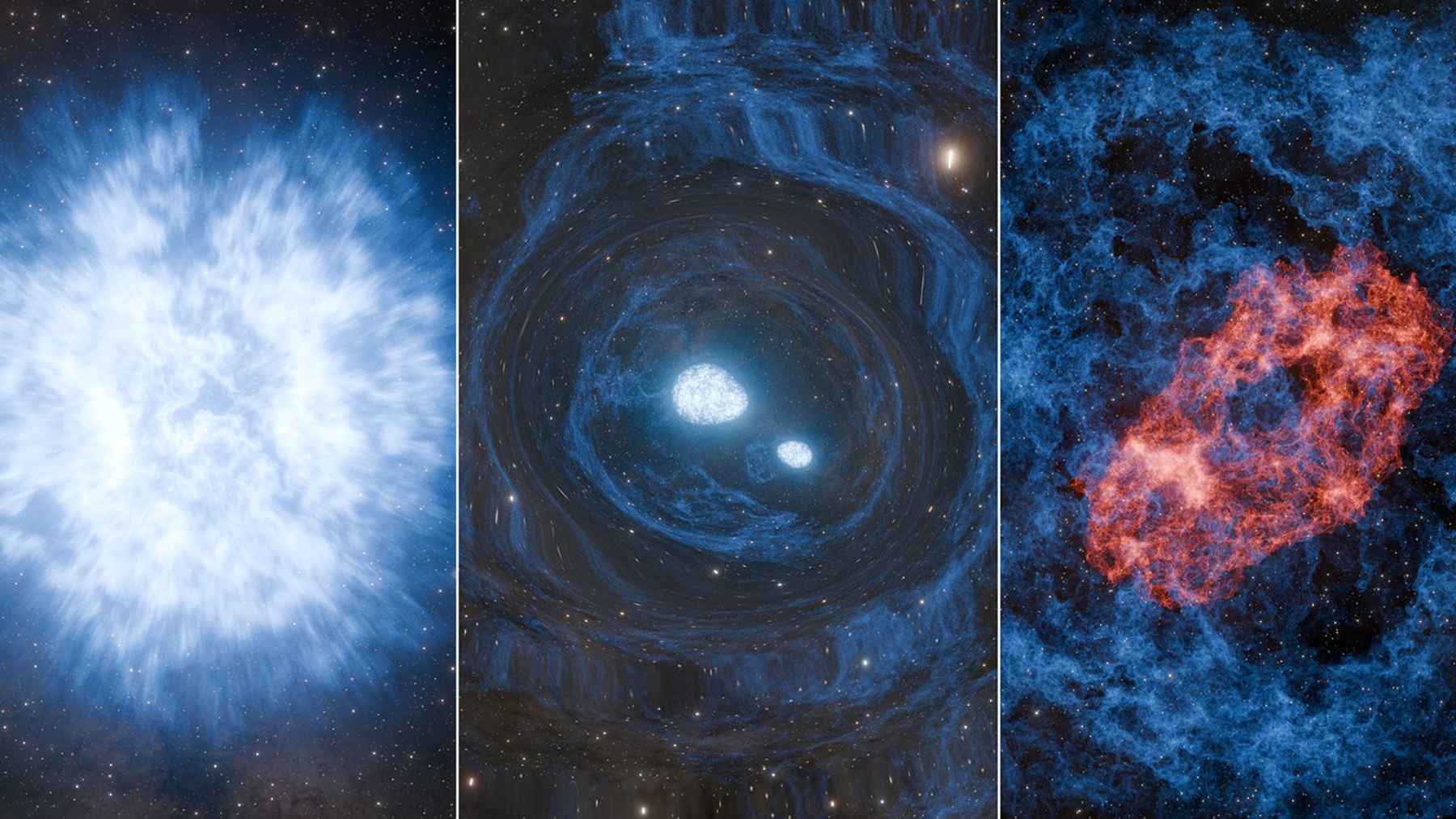
We can say that right after the Big Bang, the universe was a chaotic, superheated mix of matter, antimatter, and radiation. There were no atoms yet, just a dense field of plasma existing at unimaginable temperatures between 10²⁰ and 10³⁰ kelvin. This phase is what scientists call the radiation era, and it’s beyond most people’s comprehension.
However, it is worth remembering that even in extreme heat, the universe did not reach the maximum theoretical temperature possible: the Planck temperature (~10³² K).
Continuing its formation, the temperature of the universe began to drop, and this made possible, billions of years later, the emergence of galaxies, clusters, and the cosmic structure that we know today.
What happens if something reaches the highest temperature in the universe?
By now, you may have noticed that the highest theoretical temperature calculated by scientists is the Planck temperature (~10³² K). But why is it the limit, and how was it calculated?
To calculate this supreme limit, physicists combine a few of nature’s fundamental constants, which are gravity (G), the speed of light (c), Planck’s constant (h), and Boltzmann’s constant (k). If you’re curious, the formula looks like this:
T_P = √(c^5 * ħ / (G * k^2))
It represents the temperature where the effects of gravity become dominant. What does this mean?
Theoretically, what would happen under such extreme temperatures?
Well, scientists raise two points about what would happen when such temperatures are reached:
- The laws of physics as we know them today (including space and time) would no longer work as we understand them.
- Any extra energy that was put into this system would create micro black holes, meaning that it would no longer be possible to increase the temperature “normally”.
- These micro black holes wouldn’t last long. According to some theories, they’d evaporate almost instantly due to Hawking radiation. That happens when a pair of particles forms near the event horizon and one escapes, draining the black hole’s energy.
Beyond the early universe, what else has extremely high temperatures?
The sun is no surprise to anyone when we talk about high temperatures. To be more precise, the sun’s core reaches temperatures of around 15 million kelvin, which, when converted to Fahrenheit and Celsius, is 27 million ºF and 15 million ºC.
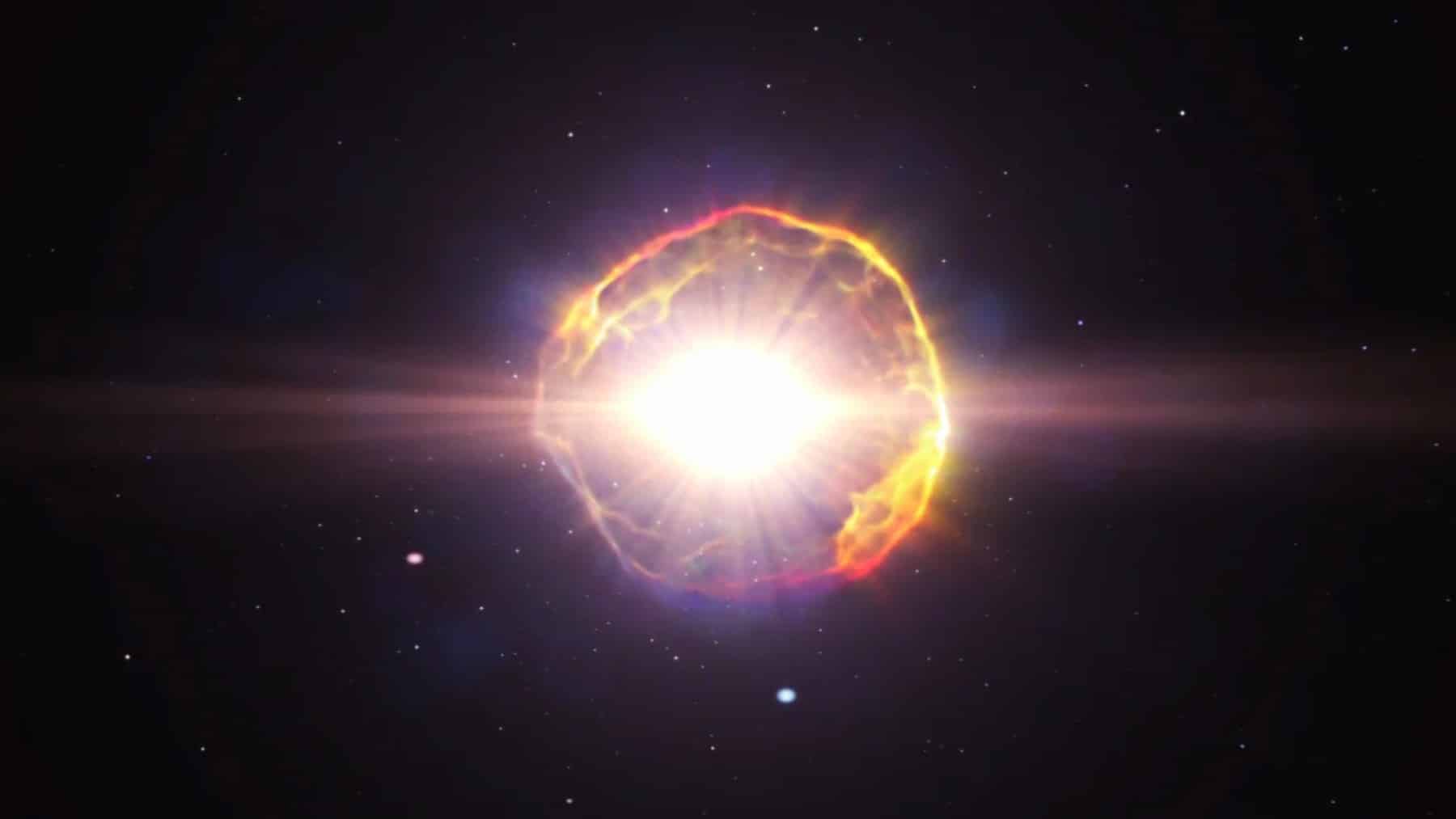
Another phenomenon that can be mentioned is very massive stars. The cores of these giants can exceed 500 million kelvin (or 900 million ºF). And just before they explode as supernovas, some may even hit 100 billion kelvin.
Scientists still don’t even know a fraction about this extreme scenario
Even though the Planck temperature (~10³² K) is unimaginable to human thought, it is possible to understand what would happen if something reached it: space-time itself would collapse, creating a scenario so extreme that our current theories simply can’t predict what happens next. And that’s when we can say that this is the end – or perhaps the beginning – of something we don’t even understand yet.
What we can conclude from all this is: even with all the advances in science, its theories, calculations and discoveries, the universe still holds many secrets. It’s no wonder that a team of astronomers recently revealed that hidden galaxies have been demonstrating strange behavior, and this could change current models of the cosmos as we know them.