As the automotive industry embraces the electric revolution, one automaker stands firm in its commitment to an engine type that has long been considered a relic of the past: the rotary engine. But now, in a fascinating new development, Mazda is breathing new life into this iconic engine with a powerful twist: laser-ignition. This advanced technology could lead to a more efficient, environmentally friendly rotary engine, ensuring the engine’s continued relevance in the age of climate consciousness. As Mazda plans to bring this laser-ignited engine to the U.S. market, there are plenty of reasons to be excited about the future of this unique propulsion system.
The return of the rotary engine
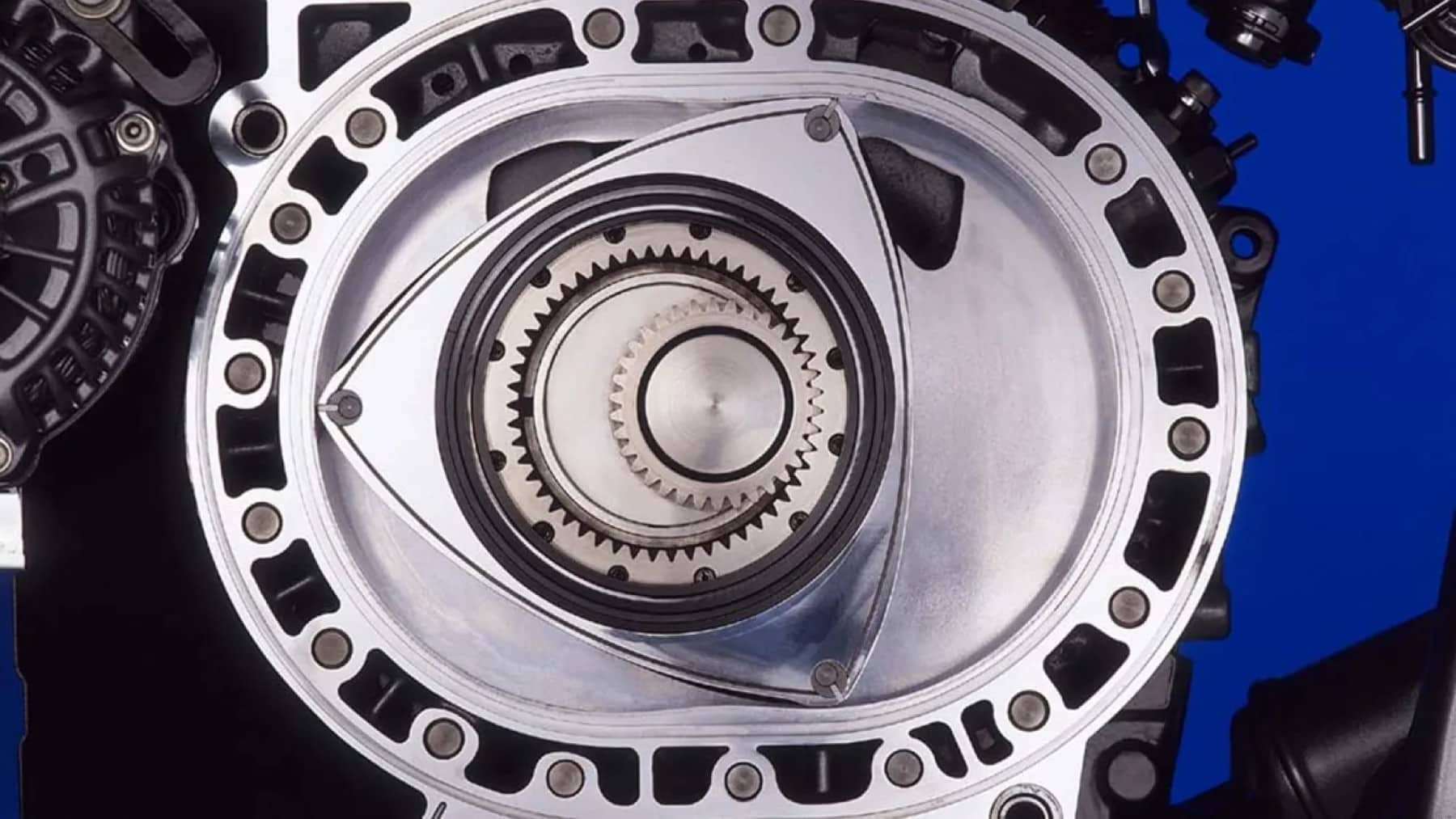
The rotary engine, an unusual and distinctive motor that gained popularity for its compact design and high-revving performance, has had a turbulent history. Mazda has long been the only manufacturer to keep the rotary alive, even as fuel efficiency and emissions standards tightened globally. Known for higher fuel and oil consumption, the rotary engine’s shortcomings in emissions have made it a tough sell in today’s climate-conscious world.
However, Mazda’s dedication to the rotary has remained steadfast. While the company has made strides in improving traditional internal combustion engines, it recognizes the need to adapt the rotary to meet stricter regulations. In a surprising move, the automaker has announced the formation of the Rotary Engine Development Group, signaling a renewed focus on revamping the rotary engine for the modern age. The latest breakthrough in this journey is the implementation of laser ignition technology.
The power of laser-ignition
At the Tokyo Auto Salon, Mazda revealed that it will utilize laser-ignition to replace traditional spark plugs in its upcoming rotary engine design. This innovation promises to revolutionize how combustion occurs within the engine. The laser system will use a tiny 9mm beam to ignite the fuel-air mixture, resulting in more precise ignition timing and improved combustion efficiency.
Laser-ignition technology isn’t new in the automotive world, but its application to the rotary engine represents a significant step forward. By eliminating spark plugs, which can be unreliable and imprecise, laser-ignition offers an ultra-precise way to control combustion. This enhanced precision leads to better fuel efficiency, lower emissions, and increased performance. The result? A cleaner, more efficient rotary engine that could appeal to environmentally conscious drivers while preserving the unique characteristics that make the rotary so beloved by enthusiasts.
A tricky position: internal combustion in the age of climate concerns
As the automotive world increasingly shifts toward electric vehicles and hydrogen-powered cars, the future of traditional internal combustion engines has become uncertain. Brands like Mazda face a delicate balancing act of maintaining their legacy of performance while adhering to the growing demand for sustainability. The rotary engine’s return, coupled with advancements like laser-ignition, shows that there is still a place for internal combustion engines, even in an era focused on clean energy.
This development raises a broader question about the future of internal combustion vehicles. Can manufacturers continue to produce high-performance engines while reducing their environmental impact? Mazda’s answer seems to be a resounding yes. While the company has made strides in hybrid technology, as seen in the MX-30 R-EV crossover, the laser-ignited rotary engine could represent a new direction for internal combustion engines. The focus isn’t on abandoning the traditional engine, but rather refining it to meet modern needs.
Mazda’s renewed commitment to the rotary engine demonstrates that internal combustion still has potential, even in the face of climate concerns. While electric vehicles undoubtedly play a crucial role in reducing emissions, internal combustion engines that evolve with cutting-edge technologies, like laser ignition, could coexist alongside EVs in a diverse automotive market.