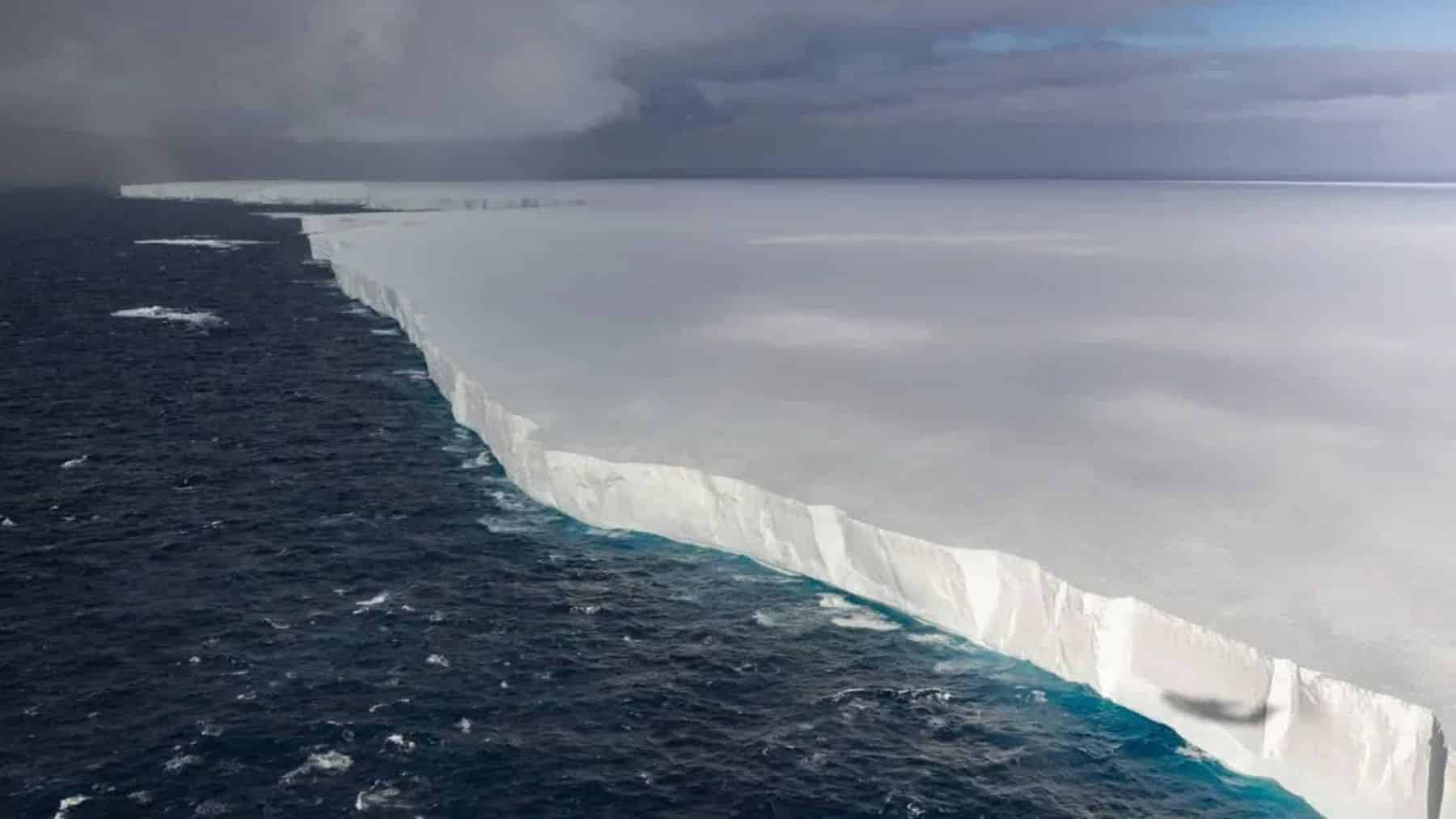
A massive A23a mega iceberg is making headlines as it heads towards a faraway island in the southern portion of the Atlantic Ocean, South Georgia. The A23a is as enormous as Rhode Island and a trillion tons. It can play a big role in disrupting the fragile ecosystem on the island.
Stuck for 40 years, now it’s on the move—here’s what happened.
The journey of A23a also highlights more global implications of climatic changes as more frequent break-offs from Antarctica into massive icebergs. The scale of A23a makes it a science of global interest because it provides valuable insights into oceanic and environmental changes. A23a calved from Antarctica’s Filchner Shelf in 1986. A23a is a natural event in which blocks of ice break loose from ice shelves. A23a is remarkable in its enormous scale, more than 1,400 miles squared.
For nearly 40 years, that enormous iceberg sat on the seabed above the continental shelf, too enormous to be shifted across shallow water. 2020, it finally detached from its position and drifted into oceanic depth. Scientists are eagerly monitoring A23a’s migration because its journey will affect global ocean currents as much as ecosystems.
South Georgia is a crucial haven for fur seals, gentoo penguins, albatrosses, and many more. Grounding A23a will also impact the breeding and feeding of these animals. If it grounds on the shallow platform on the continent, it will impact migration between breeding and feeding areas, with animals having to travel a longer distance and exerting more energy like this related research that will surprise you.
Climate change is accelerating iceberg break-offs—here’s what it means for the planet.
The timing with which A23a will affect is important. During breeding seasons, seals, as well as penguins, are more vulnerable. If food resources are flushed out from accessible regions, an enhanced death toll can be seen in these animals. However, if the iceberg arrives once breeding is complete, its impact will be negligible as pups and chicks will be more autonomous.
Global warming leads to increased frequency and greater magnitude of iceberg calving processes, particularly in ice formations such as A23a. The accelerating ocean warming along Antarctica speeds up ice shelf calving steps, thus causing extensive icebergs to split from shelf edges.
The rising tones created by this trend allow oceans to experience higher sea levels and damaged marine habitats. During high-speed deglacial periods, scientists from Utrecht University monitored how icebergs travel. These periods occur when ice ages come to an end. The researchers observe that growing ice movement behavior threatens the ocean through its effects on salt levels, thermal balance, and the ability to absorb substances.
What’s next? Experts predict where A23a will go and its long-term impact
Scientists are also making predictions regarding A23a’s likely trajectories and impact on South Georgia with computer models. The models forecast how much meltwater will be emitted from A23a into the Southern Ocean and its impact on ocean currents and carbon absorption.
The path of the movement depends heavily on the changing ocean currents and weather patterns while maintaining an unforeseeable end location. Historical icebergs from the past have followed equivalent paths, although some delivered varied consequences when they reached South Georgia. Scientific research will depend heavily on determining the course of A23a before it completes its unknown path. The observations show that increased ice movement is a risk factor because it affects ocean salinity, heat levels, and absorption processes.
The movement of mega iceberg A23a toward the South Georgia islands demonstrates a clear connection between the worldwide temperature increase and oceanic biodiversity, similar to this news on biodiversity, alongside animal life. Scientists’ tracking of its migration reminds us of the global impacts resulting from such developments and the collective measures needed to tackle global warming.