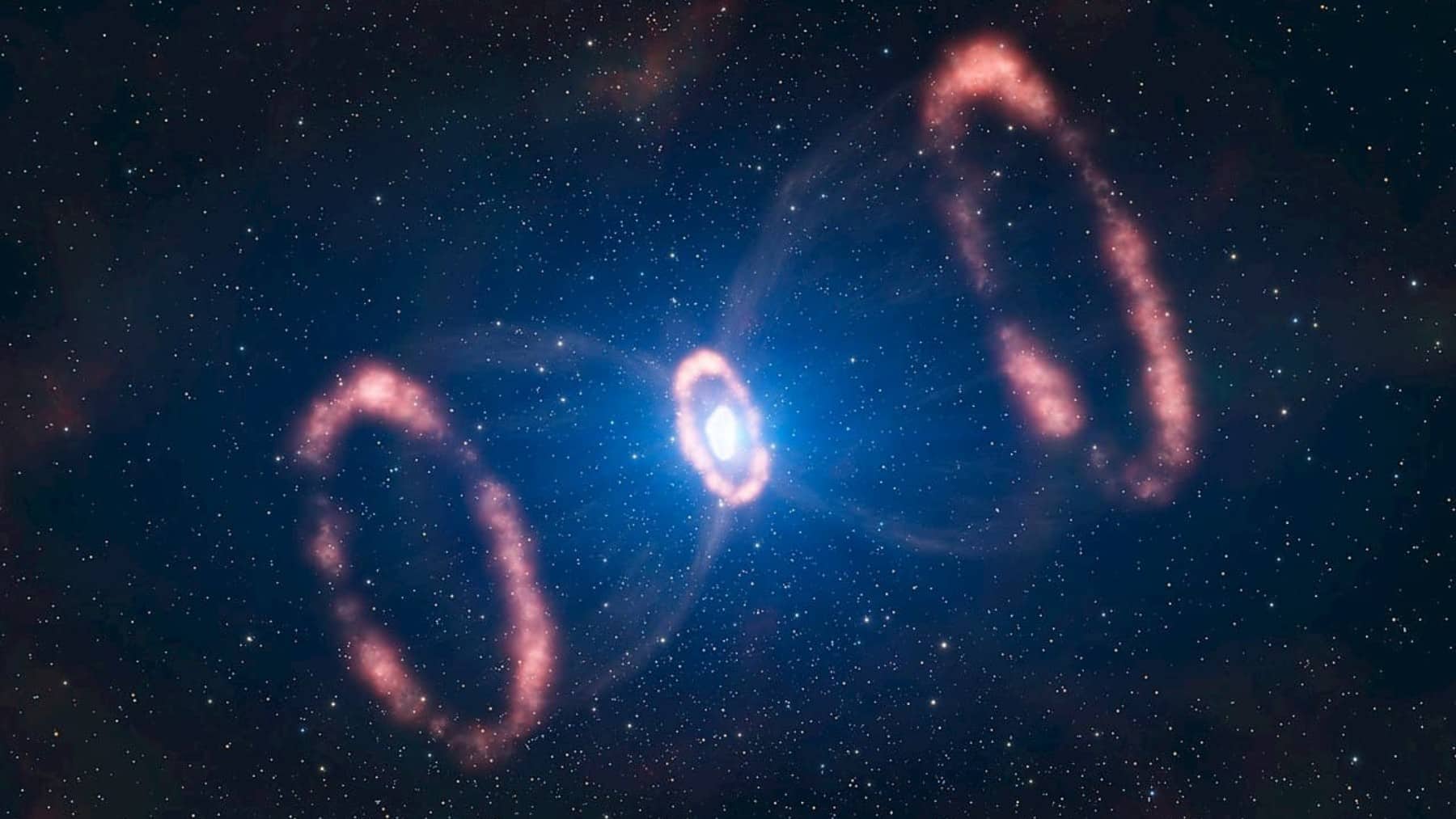
NASA has been closely monitoring the behavior of two stars in the Corona Borealis constellation for some time now. Recently, scientists noticed that these bodies were behaving somewhat strangely. They decided to investigate further and discovered that there are some changes happening to them that could cause an event never seen before in the entire universe.
What two stars are these, and where are they?
These stars are present in the constellation T Coronae Borealis, which is about 3 thousand light-years from Earth. And the most curious thing is that this constellation has been present in our analyses here on Earth for a long time. It has a very unique history of activity, even though until 2016 everything was calm – apparently, too calm.
Since 2016, astronomers have begun to notice that the constellation is changing drastically, because they noticed that it was getting brighter, in addition to acquiring an unusual bluish coloration. This behavior even reminded them of something similar that happened in 1946, when there was an explosion – yes, we may have to prepare ourselves. And which two stars make up this constellation? We are talking about:
- A red giant, which is an expanded and ageing star;
- And a white dwarf, which is nothing more than the hot and dense core remaining from a star like the Sun.
What are experts expecting from this strange behavior?
After analyzing the constellation with the Fermi space telescope, scientists were able to reveal that it appears that T Coronae Borealis is about to undergo a rather rare astronomical phenomenon called a recurrent nova. Okay, so what does that mean? Well, it will become a temporary new star that will be visible to the naked eye in the night sky.
And of course, this will happen through an explosion, it couldn’t be any other way, right? This explosion is thermonuclear and occurs when the matter stolen from the red giant accumulates on the super hot surface of the white dwarf, and this causes an explosive reaction that can increase the brightness of the system by up to 1,585 times (recently another star caught attention by revealing something inside it that no one expected).
This phenomenon has happened before, but it was a long time ago in the years 1787, 1866, and 1946, with a possible historical record in 1217. You can see that each cycle takes approximately 80 years to complete, meaning we’re very close to this happening again, even if we can’t yet give an exact date. Astronomer Sumner Starrfield and astrophysicist Javier Armentia even give us a heads-up:
“There is no way to predict exactly when it will explode. Our estimates of when it will happen soon are based on observations of its behavior just before the explosion 80 years ago. Its current behavior gives us clues, but it cannot be determined”.
The unique event that stars can cause
In addition to this explosion being fundamental for academic life itself – after all, all phenomena are observed closely – it will be sensational for the constellation T Coronae Borealis to become visible to the naked eye as a temporarily bright star in the northern hemisphere sky.
“There are some recurrent novae with very short cycles, but we don’t typically see a repeating explosion in a human lifetime.” – Rebekah Hounsell
Astronomers believe that it can shine for about a whole week, which allows us to appreciate it as much as we want, in addition to being a great time for professionals to do their analyses. Even if this phenomenon does not happen for now, it is very important to have this prediction for modern astronomy. An example of these current discoveries is the star factory recently discovered by NASA, scientists believe that this place is where the Universes are formed.