NASA is always monitoring everything related to the Universe, but now it’s different. It’s on high alert. That’s because in recent years, the agency has been monitoring a strange and growing deformation in the Earth’s magnetic field – an anomaly. We’re talking about a region where the planet’s natural magnetic force is weakening significantly… and this creates risks for satellites, spacecraft and electronic systems in orbit.
What is this anomaly that is coming to the US?
Before we say anything, we need to emphasize that the phenomenon that is happening does not pose any direct risk to life on the Earth’s surface. The consequences are directed only to space, but that does not make the problem any less real and worrying. Why? Well, according to NASA scientists, there are already some signs that the anomaly is not only growing, but is also approaching North American territory.
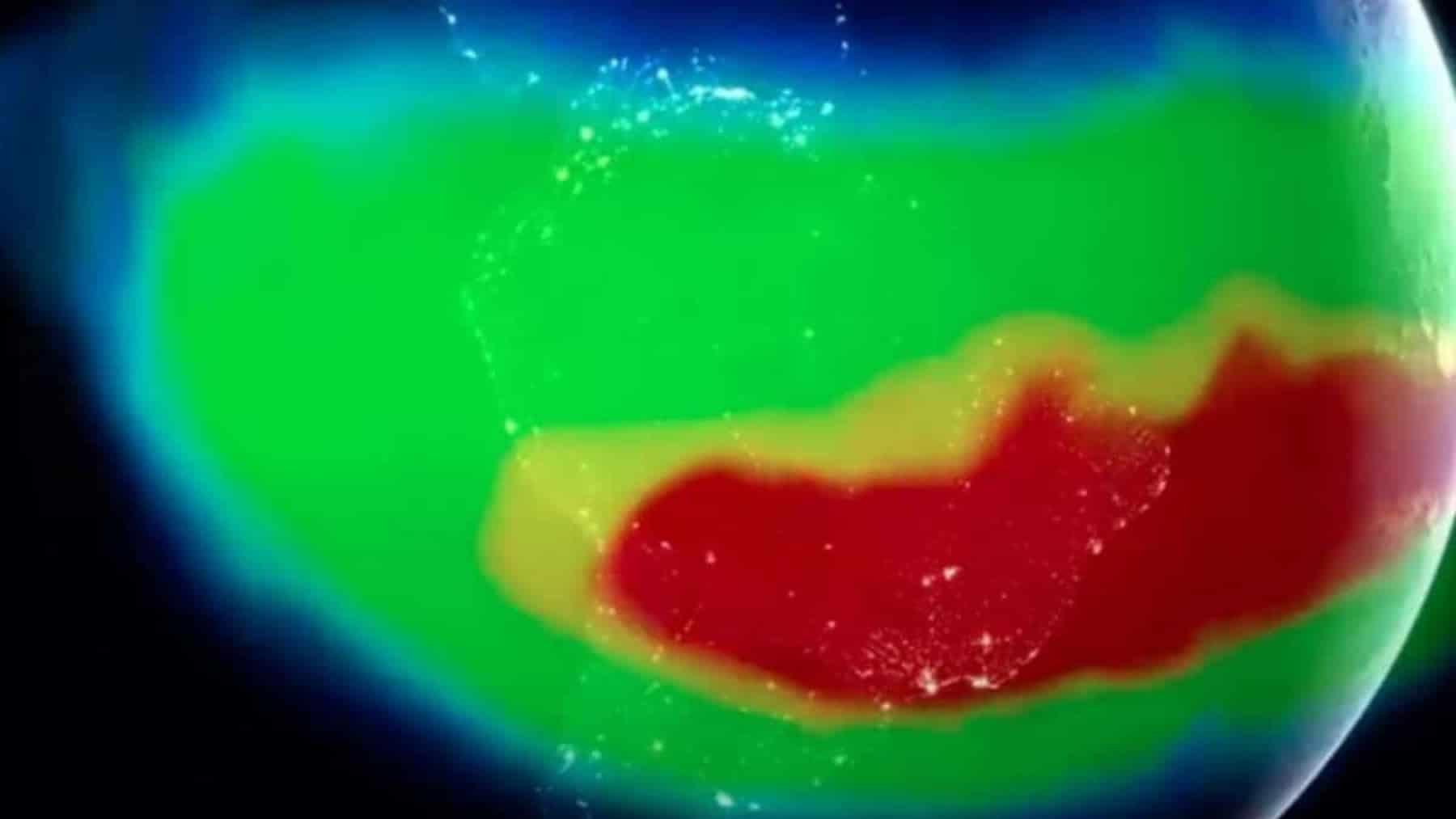
Ok, but what is this anomaly that is worrying us so much? We are talking about the South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA), which extends over part of South America and southwest Africa (but is now expanding). And what does it mean? In simple terms, it is a kind of “dent” in the Earth’s magnetic shield.
And to understand why this is so worrying, we need to remember that the magnetic field acts as a barrier against highly energetic solar particles. However, in this specific region, which covers parts of Brazil, Paraguay, Argentina, and the South Atlantic, this shield becomes weaker, allowing particles from the Sun to penetrate deeper into the atmosphere. And for all equipment orbiting the Earth, such as satellites and the International Space Station, this will mean greater exposure to radiation and a greater risk of technical failures. In other words, systems could crash, data could be corrupted, and, in the worst cases, components could be permanently damaged.
“The magnetic field is actually a superposition of fields from many current sources”, explained geophysicist Terry Sabaka of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center.
The SSA (South Atlantic Anomaly) is growing and moving
Of course, NASA deals with this in a preventive manner. They shut down non-essential systems whenever their satellites cross this critical zone. However, this problem is becoming more difficult to manage. After all, more recent studies show that the SAA is not just a static anomaly. It changes shape, intensity, and position over time. Back in 2020, for example, scientists observed that it began to divide into two distinct low-intensity cores.
In addition, the anomaly is slowly moving westward, getting closer to the Caribbean, the Gulf of Mexico, and the southeast coast of the United States. This trend worries scientists the most since more satellites in orbit over North American territory may pass through high-risk regions (after all, it is growing).
And where does this anomaly come from?
Well, the origin of the SAA is deep inside the Earth. This is because, in more technical terms, the magnetic field is generated by the movement of molten iron in the planet’s outer core. However, beneath the African continent, at a depth of about 2,900 km, there is a large mass of dense rock that disturbs this flow and weakens the field in certain regions. This, combined with the natural tilt of the Earth’s magnetic axis, causes this anomaly to appear.
Reinforcing once again, it does not pose an immediate danger to us here on the surface, but it still requires a lot of attention from space agencies, especially now that it is approaching the northern hemisphere and the USA. This phenomenon is just one more that NASA has to pay attention to; another is a galaxy that we forgot to observe for a moment, and now there is only a black hole.