Solar panels are a cornerstone of renewable energy development. Using photovoltaic technology, they convert energy from the sun into electricity. First gaining commercial development in the 1990s, solar panels have long been the face of the sustainability movement. With increased innovation and development, current technology has come a long way since it was first introduced.
How photovoltaic technology work
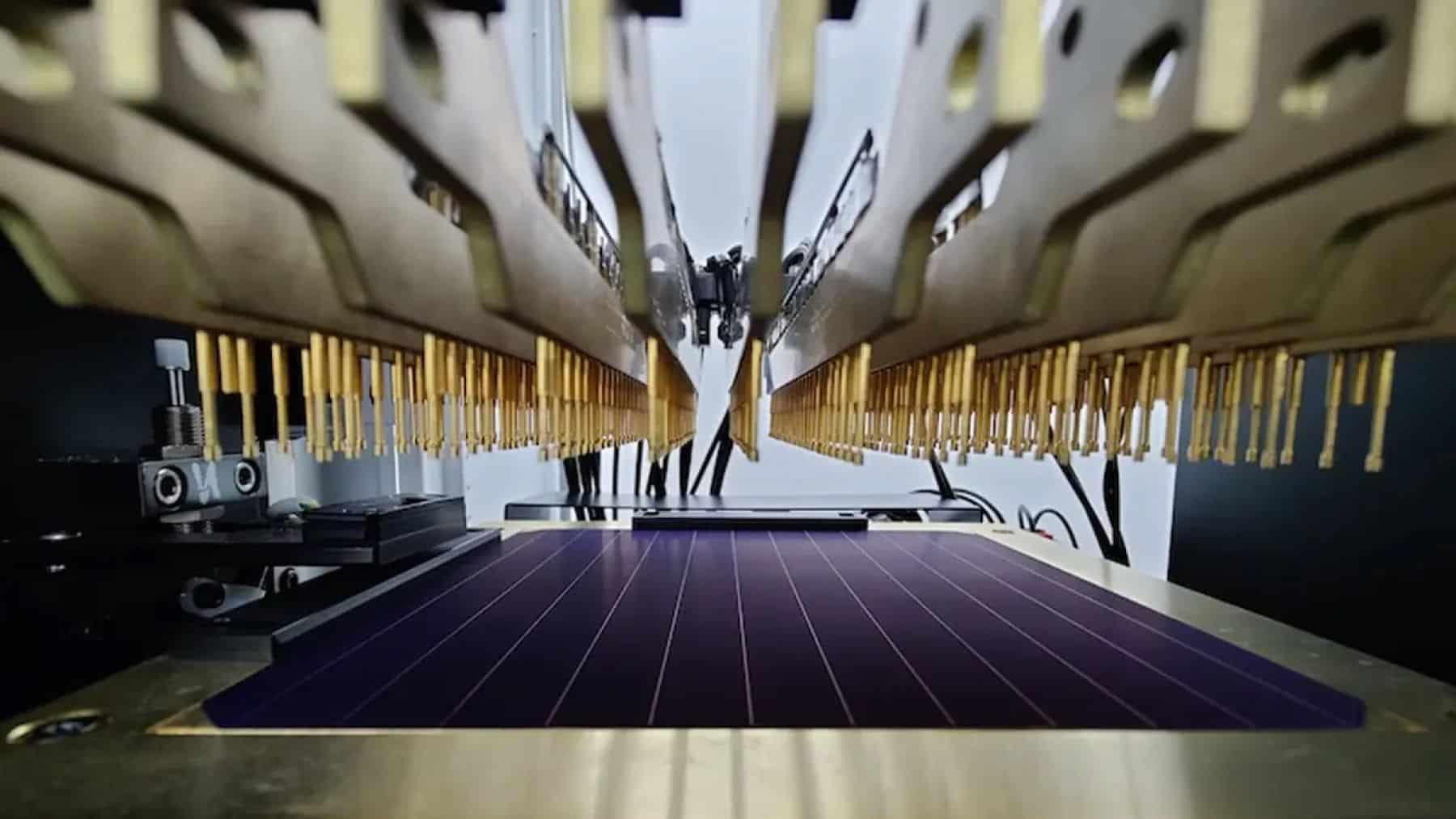
Within solar panels, there are solar cells which operate on the photovoltaic effect (hence the name). This refers to the process of how light is converted into electricity through certain materials. When sunlight hits the solar cell, it excites electrons within a semiconductor material the solar panel is made out of. These electrons then break free from their atoms, which creates electron-hole pairs The movement of the electrons generates an electric current, which is then what produces electricity to be used as a renewable power source.
This technology has been central to how solar panels operate since they were first introduced. Since then, they have been refined and improved, including for use in space operations. This new solar technology created specifically for use in space has been revolutionary for space exploration, as it provides a constant power source for space stations in space with increased efficiency and affordability.
New technology by SILVER solar cell project
One such innovation of photovoltaic technology is the SILVER solar cell project, lead by the Australian National University. While the project was completed in 2014, it has been continuously used and built upon in current photovoltaic projects. The project was intended to produce more efficient SILVER cells to improve the conversion efficiency of SILVER modules as well as lowering manufacturing costs.
The biggest advantage of the technology is that they are bifacial. This means that they can capture and convert sunlight into electricity from both cell surfaces. Solar panels are also generally produced from silicone, and the SILVER cells were demonstrated to use less silicone than conventional solar panels at the time. Today, the solar power industry is expected to account for over 50% of electricity generation by the middle of the century.
Solar power possess other opportunities for innovation
The transportation industry has also been exploring the potential for photovoltaic technology. One such innovative project is the California high-speed rail project. Initially approved in 2008, the project is still currently underway. The vision is to connect major cities across California like San Diego and Los Angeles. The plan is to have the entire train run off of solar panel technology.
“We are committed to bringing this system to life and making it as sustainable as possible,” said Brian Kelly, CEO of the California High-Speed Rail Authority.
The project has also been identified as a key component for contributing towards the economic development of Central Valley in California. The area covers over 20,00 square miles and his home to four million residents. “Connecting this area was a key component of the project’s approval,” said Kelly. This project is a key example of how renewable energy projects go beyond environmental sustainability and are key to supporting other areas of growth.
However, the train was intended to be completed in 2020, a goal which it has not achieved. To date, only 191.5 kilometers of the railway are under construction, with the total project intending to have 1,287 kilometers of railway once completed. Electrical vehicle pioneer Elon Musk has previously criticized the project, saying it is “a bullet train that is both one of the most expensive per mile and one of the slowest in the world.” This challenge of completing the project is a common theme seen across renewable energy development, as the projects often take time to lift off.