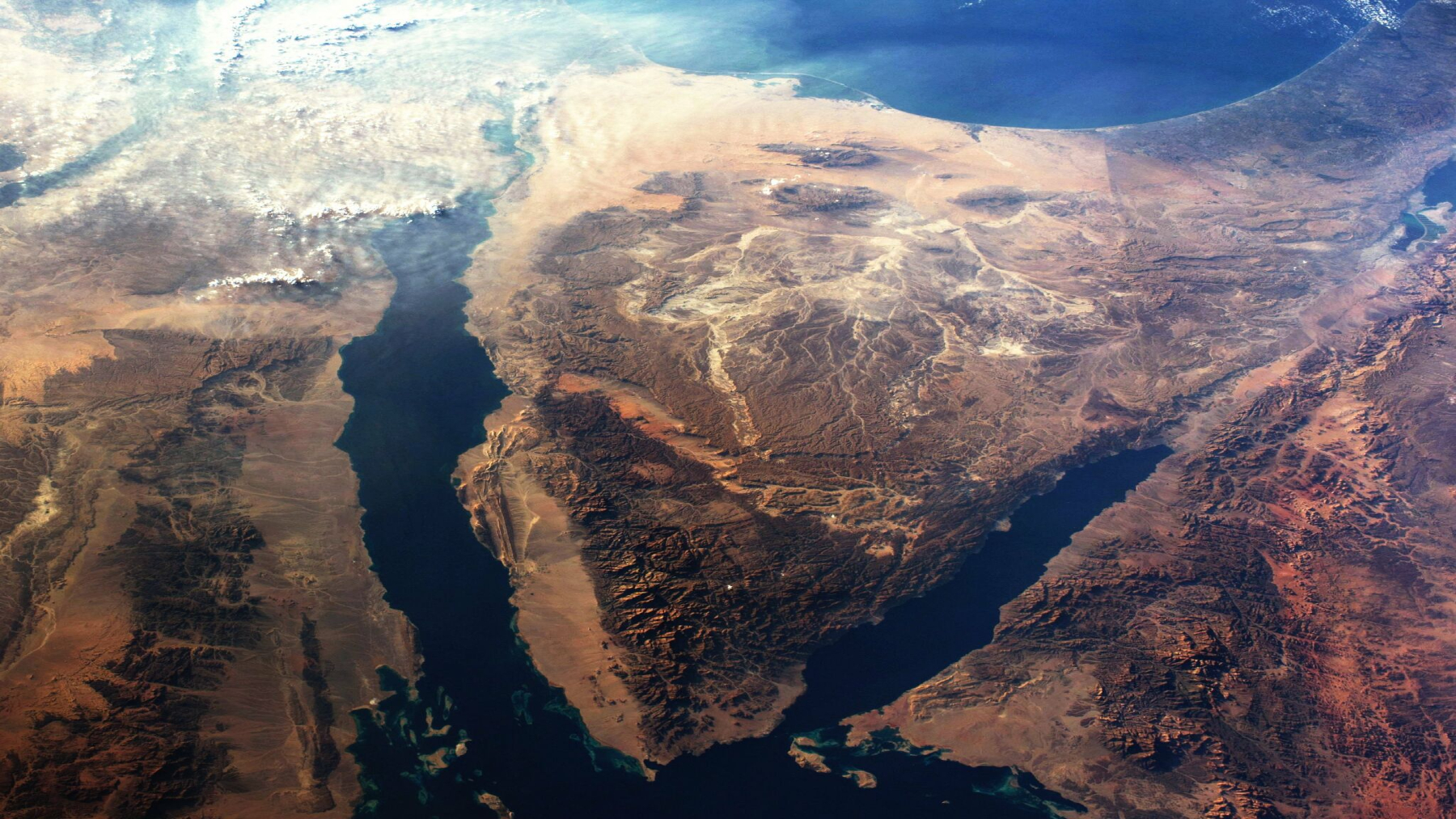
There is an enormous geological metamorphosis happening underneath the African continent. The East African Rift, a tectonic divide that runs through Ethiopia, Kenya, and Tanzania, tears the country to pave the way for the creation of a new ocean. This event, in turn, has a lot to do with the consequences for biodiversity, ecosystems, and human societies.
The East African Rift Valley: A peek into future geography
The East African Rift isn’t merely an opening in the Earth’s crust but a potential window into future geography. Over the last 30 million years, the Nubian and Somali tectonic plates have drifted apart, resulting in a huge rift valley.
This rift would then open the region to being flooded by the Gulf of Aden and the Red Sea, creating a new ocean. Geologists say the amount of time within which this transformation occurs is between 5 and 10 million years-very short time when talking about geological time.
Once this happens, countries, which are currently landlocked such as Uganda and Zambia, will have coastlines that will give way to new economic opportunities such as maritime trade and access to marine resources. However, this geological wonder may come with its challenges.
That could uproot millions of people from their homes, turn fertile lands to barren wastelands, and wreak havoc on pre-existing ecosystems. People living on the rift may consider moving elsewhere since that part of the land would become uninhabitable. The costs of creating new coastlines would also be justified by the investment cost of infrastructural development to suit environmental changes and safety against environmental risks.
Tectono forms is fueling biodiversity: Split of the species, African and Arabian
Moving tectonic plates do not restrict themselves to geography alone but propel life evolution as well. A purposed study conducted by the Institute of Evolutionary Biology (IBE) focused on how the rifting of the African and Arabian plates has affected reptilian species.
In feat, by analyzing over 430 species, the researchers managed to demonstrate via a geological split that both parts either side of the Red Sea now have distinct lineages. For example, Naja arabica (the Arabian cobra) now is assumed to be the result of divergence from Naja haje, the African cobra due to the influence of this tectonic activity. Both species used to fill the same space but then the habitats drifted apart by geographic separation, called vicariance.
The lesson majorly pertained to how tectonic forces mold biodiversity. But as the rift continues to widen, so too will new niches arise, convincing the species’ continuing adaptation to these conditions. This information is of high value to conservationists as it helps predict and ameliorate impacts that change fragmentation, and climate creates in wildlife populations.
The making of ocean: Future opportunities and possible challenges
To the human, a new ocean created has its new possibilities in offering the marine resources or expanded shipping lines. Nonetheless, the challenges of such innovations cannot be overlooked. Dislocation of communities, loss of productive land, altered climate in the region, and many more will feature in the case of consequences.
Proactive planning and international cooperation required addressing these challenges. Governments and scientists must come up with appropriate measures to combat the socio-economic and environmental effects caused by this change.
In addition, this reminds us of the dynamic nature of our planet, stressing the need to adopt sustainable development practices to align with the changing systems of the Earth. Additionally, the rifting process accentuates the need of preserving biodiversity against destruction due to such monumental changes.
It can help the study of evolutionary history of species with regards to examples that live before and after the Red Sea split to generate strategies of conserving wild animals and maintaining an ecological balance in an ever-transforming world.
There is a geological monument called the East African Rift that exhibits the dynamic nature of the earth. Although it may take time to develop a new ocean, the arrival of such a thing will surely reshape the landscapes, ecosystems, and human conditions. It shall benefit understanding of these transitions in designing their complementarity with the environment and affected people.