One of the biggest problems we face globally today regarding energy is the high rates of environmental pollution resulting from high carbon dioxide emissions from the automotive sector, a large number of factories and much more. Recently it was discovered that one of the biggest tools of recent times can also be highly polluting.
This is the big problem they are looking to solve: Innovation has clashed with energy efficiency
Well, since the whole world declared a climate emergency, thousands of factories, industries and companies have set out to decarbonise different sectors, opting for more environmentally friendly, sustainable and sustainable alternatives. However, what no one expected was that one of today’s greatest achievements would turn out to be highly polluting.
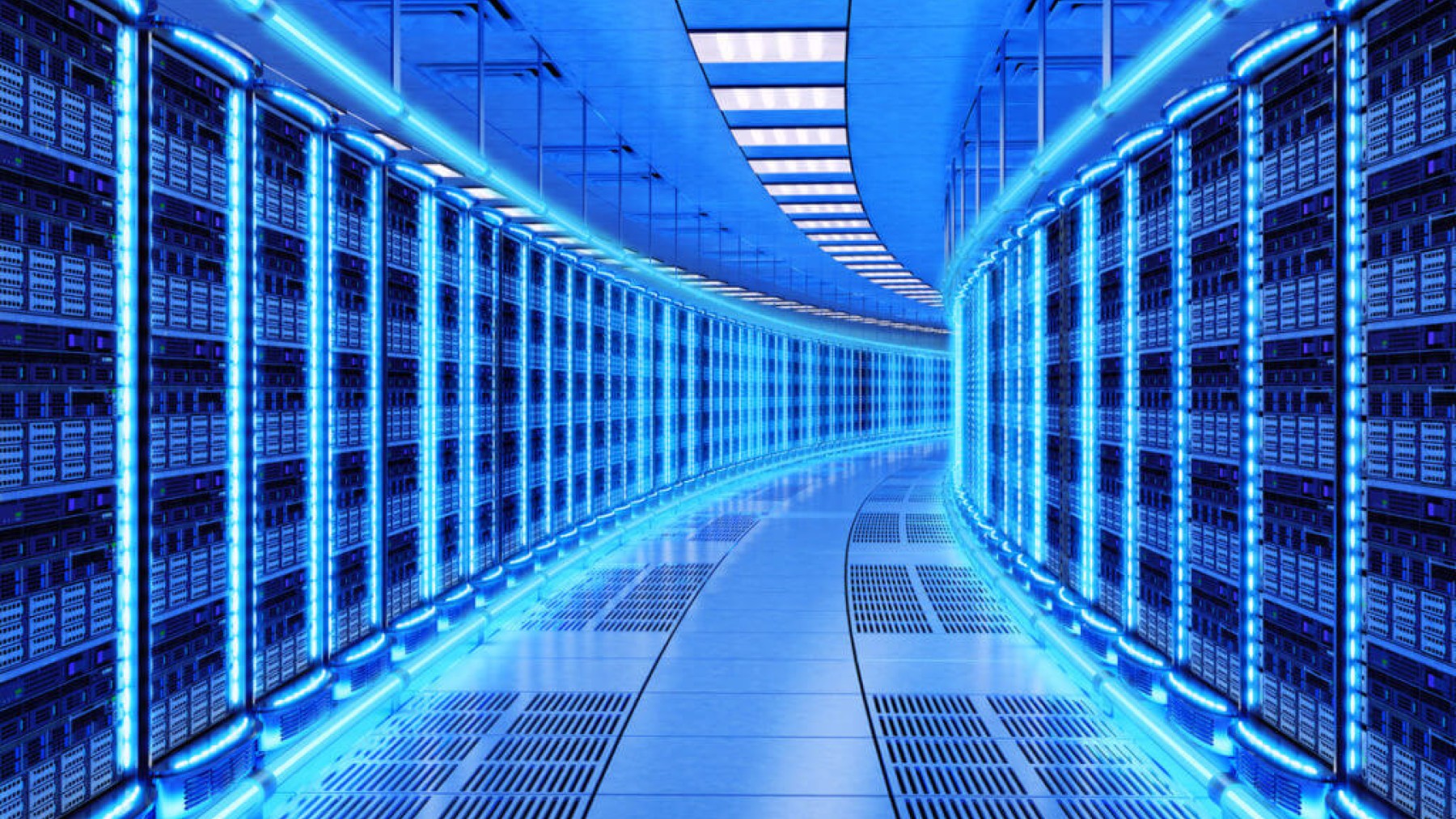
It is no news that artificial intelligence has been a great achievement and an impressive tool that most people use on a daily basis, and is even frequented by more and more companies in order to develop innovative products to offer to the public. On the other hand, what many do not know is that this generative artificial intelligence demands about 10 times more energy than traditional algorithms.
We are talking about the fact that, for Google and Microsoft, keeping and storing millions of files on a daily basis means an electricity consumption that would exceed that of 100 different countries. These two aforementioned companies individually reported a truly alarming consumption, in the year 2023 they both reported a consumption of 24 TWh.
As already mentioned, around 100 different countries spend less electricity than these corporations, among them are: Dominican Republic, Iceland, Jordan, Tunisia and Ghana. This information was reportedly compared by analyst Michael Thomas.
Alarming increases in pollutant emissions: Experts have no good news for the planet
Since 2020 both companies began to report some high percentages of carbon dioxide emissions from their plants, Microsoft reported that their emissions had increased by about 31%, while Google announced a 48% increase in the last 5 years.
Although both companies have been trying for many years to offset their high carbon emissions with renewable energy sources to help reduce their high demand, artificial intelligence still continues to put up a big fight as both companies aim to reach net zero emissions by the end of the decade.
An extremely similar situation happens with water consumption, with Google aiming to replenish more water than it uses by the end of the decade and Microsoft aiming to reduce its consumption by 95% over the next few years.
What is their solution to this delicate conflict? Google is thinking about the future
Unsurprisingly, these big companies have already set about trying to reduce the huge environmental impact they are causing. One of the best ways to reduce this excessive energy consumption is to use more renewable energy sources to provide these large power plants with their own self-consumption.
For its part, Google has developed a new project called The Four M’s, to reduce the energy demand of artificial intelligence. This is based on improving the effectiveness of hardware and machine learning models, and will also require new data centre facilities where there is an abundant flow of energy and water, the latter for good cooling of the servers.
The increasing reliance on generative artificial intelligence in our society has highlighted a new challenge in the fight against climate change: the massive energy consumption of the systems that support this technology. While artificial intelligence has been a revolutionary tool, its environmental impact cannot be ignored and large companies are already working on promising solutions.