The NASA-operated Perseverance rover continues to boost scientific interest and public fascination with Mars discoveries after its latest exploration findings. Scientists are fascinated by the round objects in a rock studied by the Perseverance rover because their discovery inspired questions about their origin and meaning. This article examines the remarkable discovery made by the Perseverance rover alongside its scientific consequences for Mars research.
This Martian rock discovery has everyone asking: What are these tiny spheres?
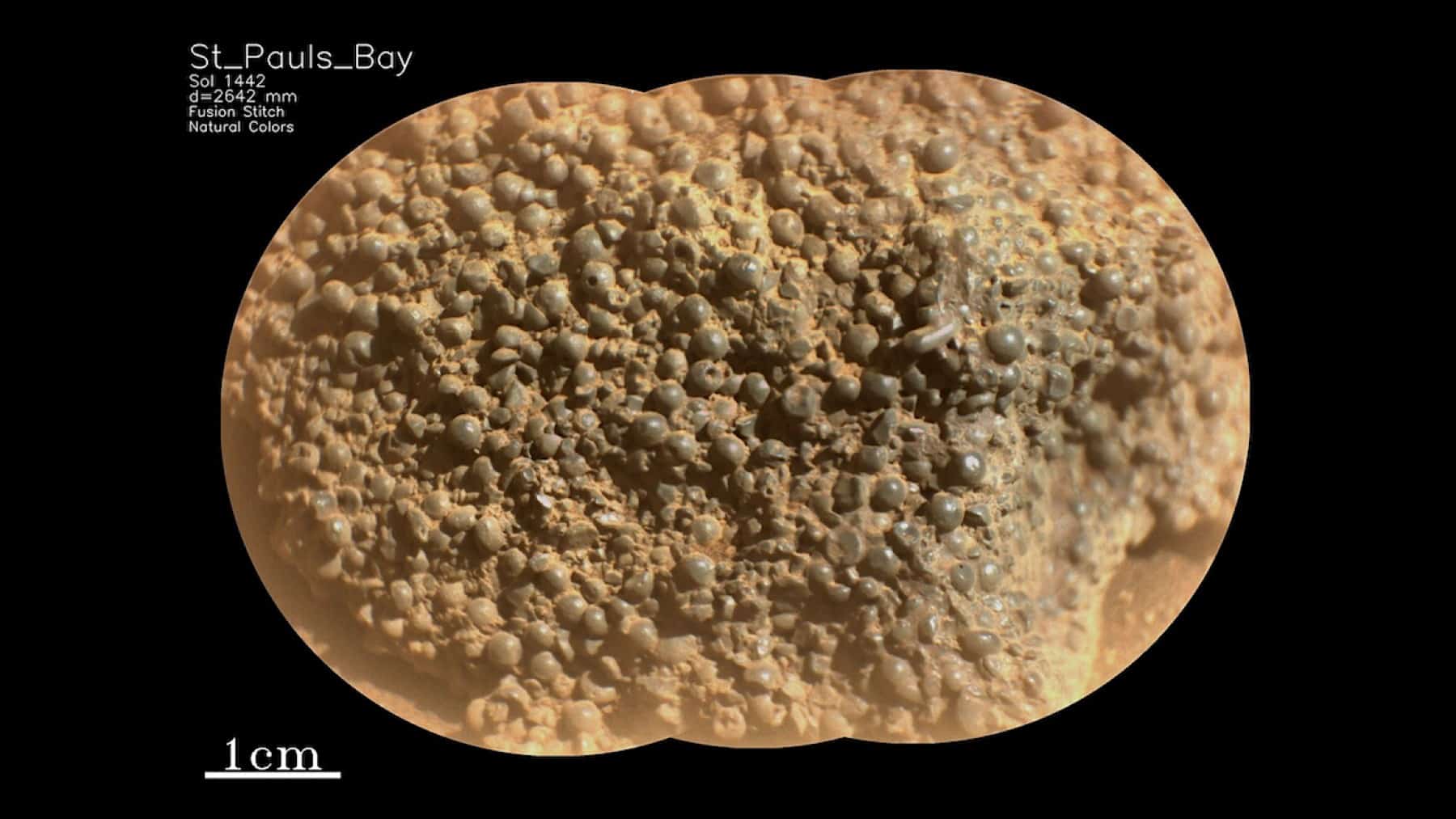
The Perseverance rover, operating under NASA, sent a picture on March 11, 2025, of a rock in the lower Witch Hazel Hill area at the Jezero crater rim. Three hundred millimeter-sized grey spheres spread across the “St. Paul’s Bay” rock surface. The rock contains spheres that range between elliptical and angular shapes and potentially stem from broken particles. In addition to their enigmatic appearance, small holes exist among several of these rounded formations.
The scientific community on Mars has recorded the presence of such spherical shapes previously. The Mars Exploration Rover Opportunity identified the “Martian Blueberries” in Meridiani Planum during the year 2004. Spherules recently discovered through the Curiosity rover presented the same characteristics when examined on rocks located in Gale Crater’s Yellowknife Bay region. The latest observations by Perseverance show popcorn texture formations in sedimentary rocks of the Neretva Vallis inlet channel.
How these Martian spheres could reveal volcanic eruptions or ancient water
Scientific research suggests concretions are the primary mechanism for sphere formation through groundwater interaction within rock pore spaces. Water-based precipitation forms spherical shapes because minerals leave the water solution to envelop a central core. Scientists have detected this formation pattern on Earth and throughout examinations of Martian samples. The occurrence of cementing processes through natural methods acts as vital evidence to support the study of planetary liquid activity.
The formation of these particular spheres stems from volcanic eruption activities, which involve droplet cooling and subsequent rock condensation following meteorite impacts on the planet. Based on the formation mechanism that led to the creation of the sphere, the geological history of the Jezero crater and Mars would be fundamentally altered. Scientists need to understand the precise source of these spheres to develop proper insights into Mars’ historical development.
Scientists believe this could change what we know about Mars’ history
The research findings in St. Paul’s Bay show potential to demonstrate key elements of the geological evolution of the Jezero crater. The research team aims to find a geological connection between the spherule-rich texture at St. Paul Bay and the overall Witch Hazel Hill stratigraphic data. The identification process will reveal if spherical shapes belong to any space-based detected dark-toned layers.
The Mars spherules create multiple mysteries regarding the possible Martian biological history. Geological investigations of Earth frequently establish microbial activity within rock accumulations; thus, the similarity between Martian and Earth formations may indicate that living organisms previously inhabited Mars. Additional research is crucial because these speculations reflect the significance of investigating this discovery further.
Perseverance is just getting started: more Martian secrets are coming
The Jezero crater remains the operational target for the Perseverance rover duties as it gathers observational samples and executes scientific experiments to discover Martian mysteries. Due to its sophisticated scientific equipment, such as the SuperCam Remote Micro-Imager (RMI) and Mastcam-Z cameras, the rover fulfills its critical investigatory functions. Scientists use data from the Mars spheres and information about their environment to better understand the geological and possible biological Martian pasts.
NASA’s Perseverance rover has discovered hundreds of millimeter-sized spheres on Mars, which remains a most exciting find for the science community worldwide. Scientific investigations of the Martian spheres will unveil Mars’s geological past and potential biological history, regardless of formation origins from groundwater action, volcanic processes, or meteorite impacts. The continuing work of Perseverance sends us opportunities to discover new science and gain a better understanding of Mars. The Martian secrets continue to hide from us as we reveal their mysteries.