Solar energy has been an essential part of growing the renewable energy sphere. Using photovoltaic energy, solar cells capture energy from the sun to be stored in a battery in order to be used as electricity into everyday application. Solar energy has been the most prevalent source of renewable energy, taking up a majority share in the clean energy market. Innovation continues to persist, with researchers investigating ways to make the solar cells themselves more renewable.
Solar energy continues to be a vital source of renewable energy
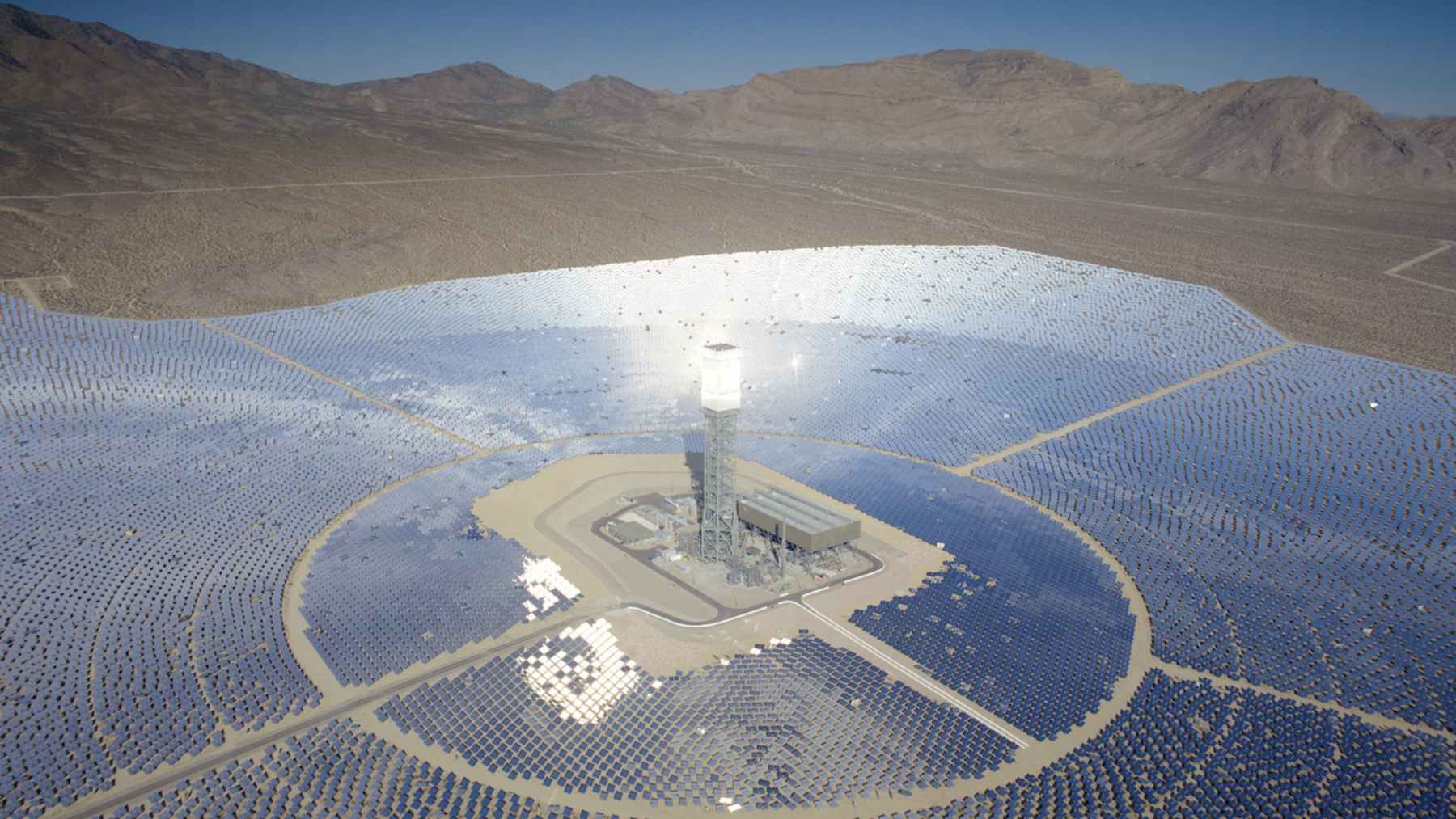
Solar energy is one of the most abundant sources of renewable energy on earth. The energy is so powerful, that if we were able to capture the full range of the solar energy for an hour and a half, it would be able to power all of our energy needs for a whole year. While we have not quite been able to reach the technological requirements needed to capture the sun’s energy to this extent, solar panels have been instrumental to capturing solar energy.
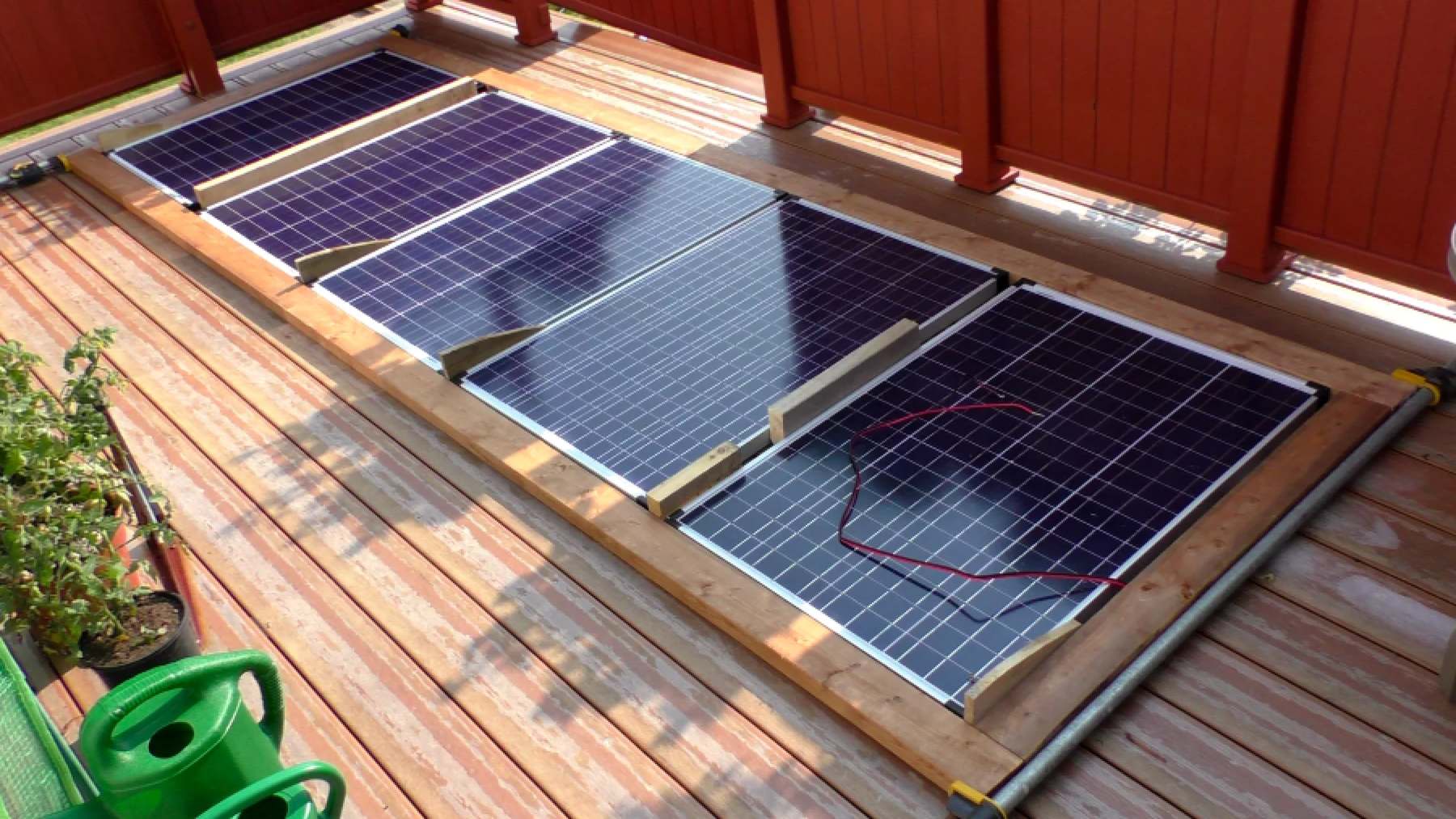
By using photovoltaic energy, solar cells capture energy from the sun and store them in batteries. One solar cell typically can capture up to one watt of energy, with a standard solar panel producing up to 400 watts of electricity per hour under optimal conditions. However, solar panels typically never reach 100% efficiency due to the variation in wavelengths throughout the day.
New possible material for solar cells
Standard solar cells in solar panels are made out of silicone. Recently, there have been proposals for these cells to be made out of different conducting materials to increase their efficiency, such as gold and silver. However, silicone is a synthetic product, which not only takes away part of the renewable aspect from the solar panel but the production of silicone material is energy intensive, with a difficult manufacturing process which can lead to hazardous chemical spills.
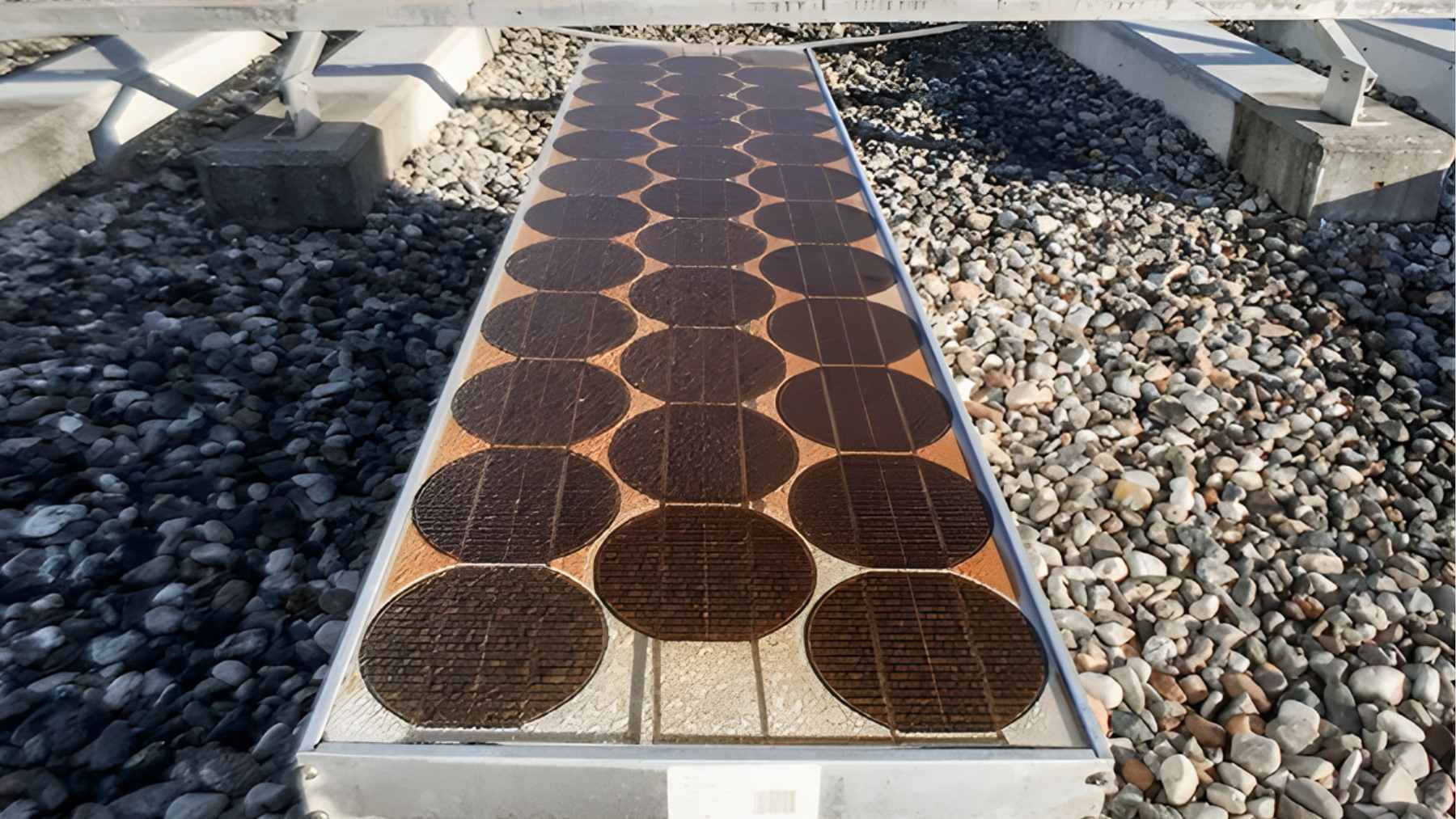
In an effort to increase the renewables and safety manufacturing process of the solar cell, researchers have been investigating the potential of organic solar cells. Not only do they have much lower production costa, but they also are light weight and flexible. Current organic solar cells are manufactured from plastic, or polymers derived from oil. While this does technically make them “organic”, they are still not good for the environment. Due to this, wood pulp is being investigated as an alternative material to produce solar cells out of.
Researchers at Linköping University and KTH have been working on developing a solar cell where parts of the cell is made out of wood pulp. According to the researchers, these small steps are to lay the foundation of the long term goal to produce a solar cell which can be made entirely out of wood pulp. Currently, the researchers are investigating if a part of the cell called the kraft lignin can be produced out of the pulp. The organic cell has, bizarrely, performed well, with decent outputs compared to its silicone counterpart:
“We want to build efficient, reliable, cheap and environmentally friendly solar cells. This study enables us to show that this is possible and a first step towards replacing today’s oil-based materials with wood-based alternatives,” says Mats Fahlman, professor at the Laboratory of Organic Electronics (LOE) at Linköping University.
Solar cell innovation continues to soar
Increasing the technological capabilities of solar cells has been essential to their continued growth. This advancement has also been seen in solar cells used in space. Solar energy is how we power the International Space Station. However, the solar panels used on the International Space Station are different to the ones we see on Earth. Most importantly, they need to be autonomous, as controlling them in space is a much more difficult procedure than the manual ones used on Earth.